Competency is a set of observable behaviors that encompass various abilities related to teams, organizations, and processes, leading to high performance and providing sustainable competitive advantages to the organization, along with knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behaviors.
Competencies are a key focus among various organizational processes related to retaining high-performing employees. Identifying and subsequently assessing these competencies guides organizations on how and where to use resources such as coaching, training programs, and incentives. When the necessary competencies for the organization are accurately defined, the selection and management of qualified personnel are carried out in a planned and targeted manner, ensuring that the right people are placed in the right positions to achieve the highest productivity.
Initially, core competencies based on organizational values and managerial competencies are defined, conveying a strong message to employees about the culture, working style, strategy, expectations for the market, and customers of the organization. Subsequently, through regular assessments of employees, discrepancies between organizational expectations and realities are identified, focusing on the most important areas that will increase job performance, employee engagement, and organizational profitability.
In this article, we will examine the core competency model of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
OECD has divided the core competencies it expects from its personnel into three main groups, which it has named as Developing Strategy, Building Relationships, and Achieving Results.
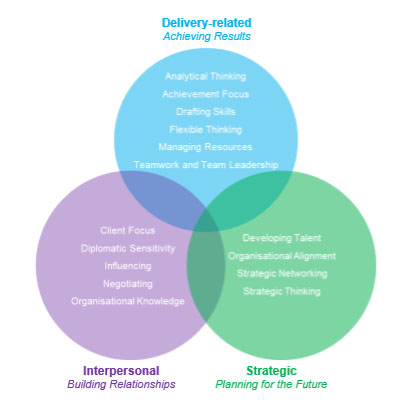
Developing Strategy
- Developing Talent
- Organizational Adaptation
- Strategic Perspective
- Strategic Relationship Management
Building Relationships
- Customer Focus
- Influence and Persuasion
- Negotiation
- Empathy
- Understanding the Organization
Achieving Results
- Analytical Thinking
- Results Orientation
- Flexibility
- Writing and Communication Skills
- Effective Resource Utilization
- Teamwork and Leadership
OECD has defined three main job families and named them as Senior Managers, Policy Research/Analysis, and Corporate Governance. For example, within the “Corporate Governance” job family, positions related to Marketing Managers, Finance Managers, Human Resources, IT, Legal, and Logistics are included.
Each position defined in the organization belongs to one of these three main groups. At the same time, positions within the organization are divided into 5 levels, and competencies and expected behaviors for each level have been determined. At the 1st level, positions such as assistants, secretaries, and operators are included, while at the 5th level, unit managers, consultants, and directors are included.
Functional competencies defined as specific technical expertise areas for each position are also specified in job descriptions and advertisements.
You can download the OECD competency model and the behavior indicators they used at this link: https://www.oecd.org/careers/competency_framework_en.pdf
Using F4e, you can easily define your own competency model, associate it with positions, and regularly measure your employees’ competencies. With the smart reporting we provide, both your managers and human resources department can track competency development on an individual and person-specific basis, ensuring that necessary actions are taken.








